Accounting professionals have a materiality guideline which allows a company to make an exception to an accounting principle if the amount in question is insignificant. So let’s head back to our Hupana Running Company and review their raw materials by cost and quantity to see where differences might occur, and how we calculate spending variances or quantity variances. Both are important and are used to calculate the overall spending variance. A cost variance measures how well the business is keeping the costs of materials and labor within the set standards. Learn how to calculate, analyze, and apply direct material variance for effective cost control and improved financial performance. Reporting the absolute value of the number (without regard to the negative sign) and a “Favorable” label makes this easier for management to read.
Direct Materials Price Variance FAQs
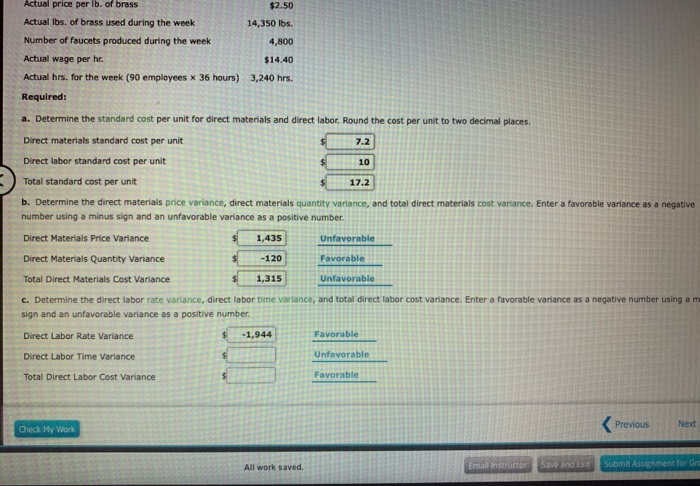
- The actual cost less the actual quantity at standard price equals the direct materials price variance.
- If there is no difference between the actual quantity used and the standard quantity, the outcome will be zero, and no variance exists.
- In this case, the actual price per unit of materials is $6.00, the standard price per unit of materials is $7.00, and the actual quantity used is 0.25 pounds.
- In a movie theater, management uses standards to determine if the proper amount of butter is being used on the popcorn.
- Assume your company’s standard cost for denim is $3 per yard, but you buy some denim at a bargain price of $2.50 per yard.
In this case, the actual price per unit of materials is $9.00, the standard price per unit of materials is $7.00, and the actual quantity used is 0.25 pounds. Because the company uses 30,000 pounds of paper rather than the 28,000-pound standard, it loses an additional $20,700. To compute the direct materials price variance, subtract the actual cost of direct materials ($297,000) from the actual quantity of direct materials at standard price ($310,500).
What is the interpretation of a direct materials price variance?
For Jerry’s Ice Cream,the standard quantity of materials per unit of production is 2pounds per unit. Thus the standard quantity (SQ) of 420,000 poundsis 2 pounds per unit × 210,000 units produced and sold. Another advanced technique is the application of statistical methods, such as regression analysis, to understand the relationship between different variables affecting material costs. By analyzing historical data, businesses can identify key drivers of variances and quantify their impact.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
Companies must stay informed about market trends and consider strategies such as hedging or long-term contracts to mitigate these risks. To begin with, calculating direct material variance involves comparing the standard cost of materials to the actual cost incurred. This comparison helps businesses understand whether they are spending more or less than anticipated on raw materials. The standard cost is typically derived from historical data, industry benchmarks, or predetermined budgets, while the actual cost is recorded during the production process.

Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Module 10: Cost Variance Analysis
Irrespective of who appears to be responsible at first glance, the variance should be brought to the attention of concerned managers for quick and timely remedial actions. The standard price of materials purchased by Angro is $2.00 per kg and standard quantity of materials allowed to produce a unit of product is 1.5kg. During December 2020, 5,000 units were produced using 8,000kgs of direct materials. Calculate direct materials quantity variance and also indicate whether it is favorable or unfavorable.
A debit balance is an unfavorable balance resulting from more direct materials being used than the standard amount allowed for the good output. Material variance is the difference between the actual cost of direct materials and the expected cost of those materials. Direct materials quantity variance is also known as direct material usage or volume variance. If the direct labor is not efficient when producing the good output, there will be an unfavorable labor efficiency variance. That inefficiency will likely cause additional variable manufacturing overhead which will result in an unfavorable variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance. If the inefficiencies are significant, the company might not be able to produce enough good output to absorb the planned fixed manufacturing overhead costs.
This investigative approach ensures that corrective actions are targeted and effective. Another element this company and others must consider is a direct disputing an invoice materials quantity variance. Let’s say your custom blankets are made of a rich acrylic and polyester blend that keeps the blanket soft for years.
The direct material variance is the difference between the standard cost of materials resulting from production activities and the actual costs incurred. This measurement is derived as part of a standard costing system, and is intended to assist management in controlling costs. The direct material variance is comprised of two other variances, which are noted below. It is customary to calculate and report these two variances separately, so that management can determine if variances are caused by purchasing issues or manufacturing problems.
Undertaking a variance analysis and understanding how you got the result you did will allow you to budget and strategize more effectively for the future. An unfavorable variance occurs when the cost to produce something is greater than the budgeted amount. Standard direct material usage refers to the amount of materials allowed to be used per unit produced. There can be either a price variance or a quantity variance, but there can also be a combination that creates the spending variance. When we talk about expected material costs and actual material costs we need to consider a couple of factors.
